If you are trying to run LLMs on AMD Instinct MI200 (MI210/MI250) cards, you have probably already experienced the pain of “HSA errors,” random segmentation faults, or containers that just hang forever.
We went through the struggle of finding the right Docker image so you don’t have to. Here is the definitive, battle-tested guide to running an OpenAI-compatible API for Qwen (14B) on ROCm.

The MI200 is a beast, but it uses the gfx90a architecture. Most “bleeding edge” Docker images today are optimized for the newer MI300 (gfx942). If you try to run the latest vLLM (0.11.x) with the default settings, it will crash because the new execution engine (aiter) isn’t fully compatible with MI200 yet.
We are going to use a stable setup that disables the experimental features and just runs fast.
Prerequisites
- Host OS: Linux with ROCm kernel drivers installed (
rocm-dkms). - Docker: Installed and running.
- GPU: AMD Instinct MI200 series (MI210, MI250/X).
Don’t use latest. Don’t use 0.11.x. We are using vLLM 0.10.1 on ROCm 6.4. It provides the best balance of modern model support (like Qwen 2.5) and stability.
Copy and paste this exact command.
docker run -it --rm \
--device /dev/kfd \
--device /dev/dri \
--group-add video \
--ipc=host \
--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE \
--security-opt seccomp=unconfined \
-p 48700:8000 \
-e HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN="your_hf_token_here" \
-e VLLM_USE_V1=0 \
-v ~/.cache/huggingface:/root/.cache/huggingface \
--name qwen-server \
rocm/vllm:rocm6.4.1_vllm_0.10.1_20250909 \
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct \
--dtype float16 \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.90 \
--max-model-len 32768 \
--tensor-parallel-size 1 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8000
Why these flags matter
VLLM_USE_V1=0: This is the most important line. The new “V1” engine in vLLM crashes on MI200 when loading JIT kernels. We force the legacy engine (V0) for rock-solid stability.--dtype float16: We don’t trustautomode on ROCm containers. Explicitly telling it to use float16 prevents initialization stalls.--security-opt seccomp=unconfined: AMD GPUs need direct memory access that Docker blocks by default. Without this, you get permission errors.- The Model Size (14B): We chose 14B because the 32B model (at float16) requires ~64GB of VRAM just for weights. On a single GPU, you’ll hit OOM (Out Of Memory) instantly once you add the KV cache. 14B sits in the “sweet spot”—fast, smart, and leaves room for context.
Step 2: Testing the API
Once the container says Application startup complete, your API is live on port 48700.
You can test it with curl. Note: Be careful with your JSON syntax! Use straight quotes ("), not curly smart quotes (“), or the API will throw a 400 Bad Request error.
Here is a test command with a complex System Prompt (as requested in our logs):
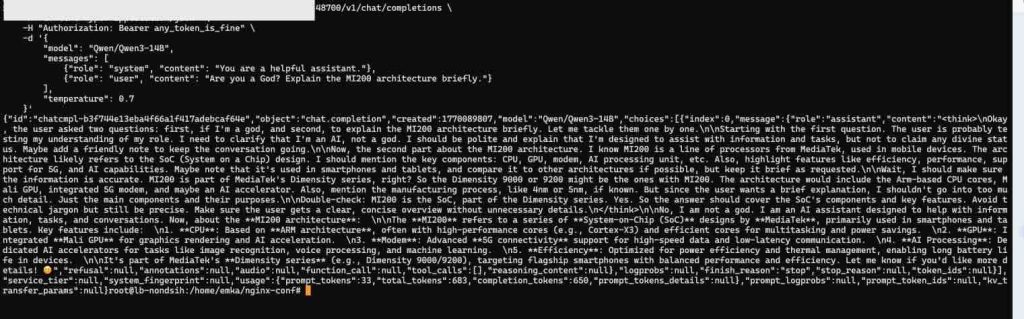
curl http://localhost:48700/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer any_token_is_fine" \
-d '{
"model": "Qwen/Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please answer in JSON format."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Are you running on an AMD GPU?"
}
],
"temperature": 0.7
}'
Note: If you are using a custom model name (like Qwen3), make sure the "model" field in your JSON matches exactly what you passed in the Docker command.
Troubleshooting
1. It hangs at “Loading model weights…”
- Cause: ROCm is compiling kernels (JIT) for your specific GPU.
- Fix: Wait. On the very first run, this can take 2–5 minutes. Subsequent runs will be instant.
2. RuntimeError: Engine core initialization failed
- Cause: You forgot
VLLM_USE_V1=0. - Fix: Add the env var. The V1 engine tries to use
aiterlibraries optimized for MI300, which segfault on MI200.
3. HIP out of memory
- Cause: Your model is too fat.
- Fix: If you absolutely need a 32B or 70B model, you must use Quantization. Change the docker command to use an AWQ model:Bash
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct-AWQ --quantization awq

