Have you ever wondered how to make your website smart enough to answer questions based on your own documents? It sounds like magic, but it is actually code! Today, we are going to explore how to combine the power of Laravel with Artificial Intelligence to build a chatbot that can read files and answer specific questions about them using a technique called RAG, or Retrieval-Augmented Generation.
To start this project, we are not just asking an AI to write code for us; we are actually integrating AI brains inside our PHP application. The goal is to build a system where a user can upload a document, such as a company travel policy, and then ask questions like “How much can I spend on a hotel in Chicago?” The application will read the document, find the specific answer, and reply in a human-friendly way. For our setup, we are using the Laravel framework, Livewire for the interactive elements on the screen, and the OpenAI API to handle the intelligence part. We also use standard PHP classes to manage the logic without needing too many complicated external tools.
The first step in this process is handling the file upload. When a user uploads a text file or a PDF via the PolicyController, the file is saved to the private storage folder, and a record is created in the database. However, the computer cannot understand the whole file instantly. We need to process it. We trigger a “pipeline” of actions, starting with a Job called ExtractPolicyText. This service reads the raw content of the file. If it is a text file, it uses standard PHP functions, but different logic can be added for PDFs or Word documents. Once the text is extracted, we update the database and move to the next critical step.
Because Artificial Intelligence models have a limit on how much text they can read at once, we cannot just send a 100-page document to ChatGPT. We must break the text down into smaller pieces. This process is called “chunking.” We use a ChunkerService to split the text into chunks of about 2,000 characters. It is very important to include a small “overlap” of text between these chunks so that we do not cut off a sentence in the middle and lose the context. Each of these chunks is then saved into our database. This prepares the data for the most mathematical part of the project.
Now we need to translate these text chunks into a language that the computer understands, which consists entirely of numbers. This is called creating “embeddings.” We run a job called EmbedPolicyChunksJob, which sends our text chunks to the OpenAI API. The API returns a “vector,” which is a long list of numbers that represents the meaning of that text. We save these vectors as JSON data in our database. Later, when we search for answers, we are not matching exact words; we are comparing these number lists to find text that has a similar meaning.
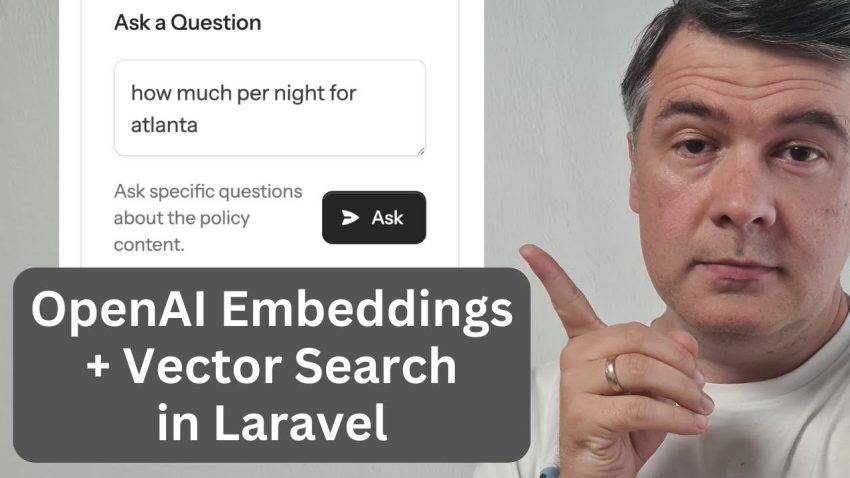
Finally, we build the chat interface using a Livewire component. When a user types a question, we do not send it directly to the AI just yet. First, we must convert the user’s question into an embedding vector as well. Then, we use a logic called “Cosine Similarity” in our VectorSearchService to compare the numbers of the question with the numbers of all our document chunks. The system finds the chunks that are most mathematically similar to the question. We take those specific text chunks and send them to OpenAI with a prompt that says, “Using this information, answer the user’s question.” This allows the AI to give an accurate answer based exactly on the data we uploaded.
Building an AI chatbot might seem intimidating at first, but it is really just a series of logical steps: uploading, chunking, turning text into numbers, and comparing those numbers. By using Laravel’s robust queue system and services, we can manage this complex flow efficiently. While this example uses simple local databases and PHP for calculations, professional projects might use specialized Vector Databases like PostgreSQL with pgvector for better performance. This project gives you a solid foundation to start understanding how modern AI features are built into web applications.